By Bruce Mountain, Victoria University and Mark Lintermans, University of Canberra
The controversial Snowy 2.0 project has mounted a major hurdle after the New South Wales government announced approval for its main works.
The pumped hydro venture in southern NSW will pump water uphill into dams and release it when electricity demand is high. The federal government says it will act as a giant battery, backing up intermittent energy from by wind and solar.
We and others have criticised the project on several grounds. Here are six reasons we think Snowy 2.0 should be shelved.
1. It’s really expensive
The federal government announced the Snowy 2.0 project without a market assessment, cost-benefit analysis or indeed even a feasibility study.
When former Prime Minister Malcolm Turnbull unveiled the Snowy expansion in March 2017, he said it would cost A$2 billion and be commissioned by 2021. This was revised upwards several times and in April last year, Snowy Hydro awarded a A$5.1 billion contract for partial construction.
Snowy Hydro has not costed the transmission upgrades on which the project depends. TransGrid, owner of the grid in NSW, has identified options including extensions to Sydney with indicative costs up to A$1.9 billion. Massive extensions south, to Melbourne, will also be required but this has not been costed.

2. It will increase greenhouse gas emissions
Both Snowy Hydro Ltd and its owner, the federal government, say the project will help expand renewable electricity generation. But it won’t work that way. For at least the next couple of decades, analysis suggests Snowy 2.0 will store coal-fired electricity, not renewable electricity.
Snowy Hydro says it will pump the water when a lot of wind and solar energy is being produced (and therefore when wholesale electricity prices are low).
Read more: Snowy 2.0 is a wolf in sheep’s clothing – it will push carbon emissions up, not down
But wind and solar farms produce electricity whenever the resource is available. This will happen irrespective of whether Snowy 2.0 is producing or consuming energy.
When Snowy 2.0 pumps water uphill to its upper reservoir, it adds to demand on the electricity system. For the next couple of decades at least, coal-fired electricity generators – the next cheapest form of electricity after renewables – will provide Snowy 2.0’s power. Snowy Hydro has denied these claims.

3. It will deliver a fraction of the energy benefits promised
Snowy 2.0 is supposed to store renewable energy for when it is needed. Snowy Hydro says the project could generate electricity at its full 2,000 megawatt capacity for 175 hours – or about a week.
But the maximum additional pumped hydro capacity Snowy 2.0 can create, in theory, is less than half this. The reasons are technical, and you can read more here.
It comes down to a) the amount of time and electricity required to replenish the dam at the top of the system, and b) the fact that for Snowy 2.0 to operate at full capacity, dams used by the existing hydro project will have to be emptied. This will result in “lost” water and by extension, lost electricity production.
4. Native fish may be pushed to extinction
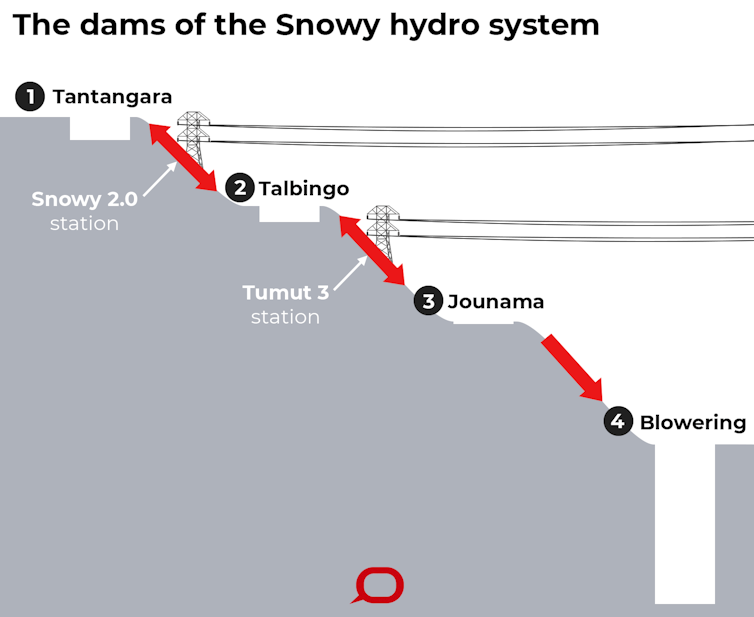
Snowy 2.0 involves building a giant tunnel to connect two water storages – the Tantangara and Talbingo reservoirs. By extension, the project will also connect the rivers and creeks connected to these reservoirs.
A small, critically endangered native fish, the stocky galaxias, lives in a creek upstream of Tantangara. This is the last known population of the species.

An invasive native fish, the climbing galaxias, lives in the Talbingo reservoir. Water pumped from Talbingo will likely transfer this fish to Tantangara.
From here, the climbing galaxias’ capacity to climb wet vertical surfaces would enable it to reach upstream creeks and compete for food with, and prey on, stocky galaxias – probably pushing it into extinction.
Snowy 2.0 is also likely to spread two other problematic species – redfin perch and eastern gambusia – through the headwaters of the Murrumbidgee, Snowy and Murray rivers.
Read more: Snowy 2.0 threatens to pollute our rivers and wipe out native fish
5. It’s a pollution risk
Snowy Hydro says its environmental impact statement addresses fish transfer impacts, and potentially serious water quality issues.
Four million tonnes of rock excavated to build Snowy 2.0 would be dumped into the two reservoirs. The rock will contain potential acid-forming minerals and other harmful substances, which threaten to pollute water storages and rivers downstream.
When the first stage of the Snowy Hydro project was built, comparable rocks were dumped in the Tooma River catchment. Research in 2006 suggested the dump was associated with eradication of almost all fish from the Tooma River downstream after rainfall.

6. Other options were not explored
Many competing alternatives can provide storage far more flexibly for a fraction of Snowy 2.0’s price tag. These alternatives would also have far fewer environmental impacts or development risks, in most cases none of the transmission costs and all could be built much more quickly.
Expert analysis in 2017 identified 22,000 potential pumped hydro energy storage sites across Australia.
Other alternatives include chemical batteries, encouraging demand to follow supply, gas or diesel generators, and re-orienting more solar capacity to capture the sun from the east or west, not just mainly the north.
Where to now?
The federal government, which owns Snowy Hydro, is yet to approve the main works.
Given the many objections to the project and how much has changed since it was proposed, we strongly believe it should be put on hold, and scrutinised by independent experts. There’s too much at stake to get this wrong.
Read more: Five gifs that explain how pumped hydro actually works
Bruce Mountain, Director, Victoria Energy Policy Centre, Victoria University and Mark Lintermans, Associate professor, University of Canberra
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
RELEASED THIS WEEK TODAY’S FEATURED BOOK:

